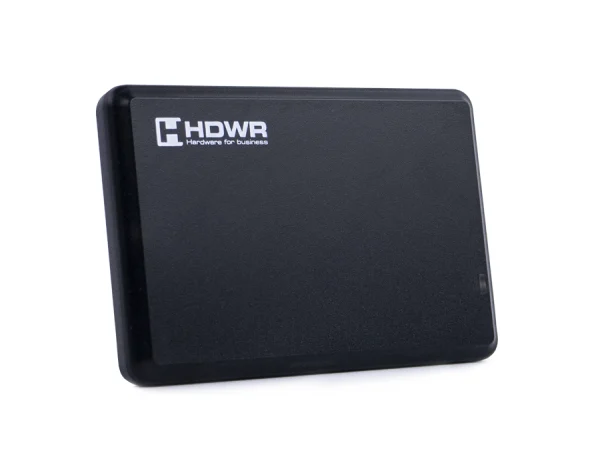
Clear Filters
Clear Filters
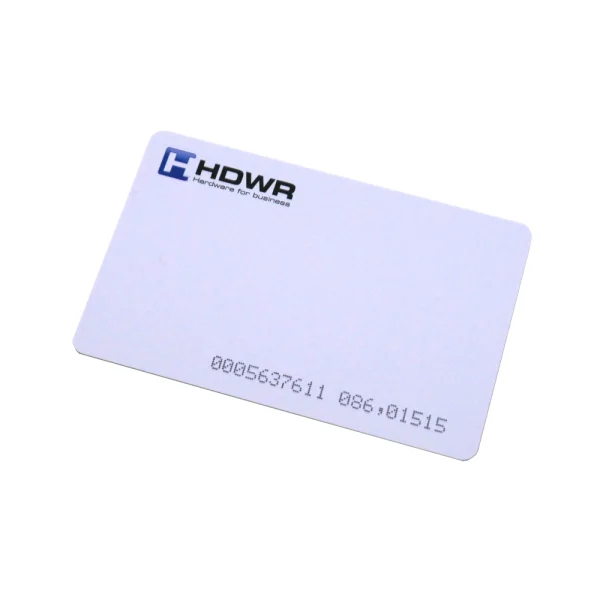
Operating frequency: 125 kHz
Material: PVC
Finish: white gloss with HDWR logo
Chip included: TK4100
Operating Frequency: 125 kHz
Material: PVC
Finish: white gloss
Device Dimensions: 86 x 54 x 1 mm
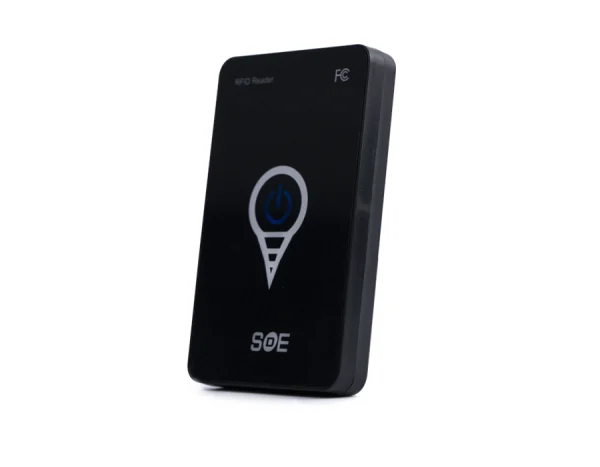
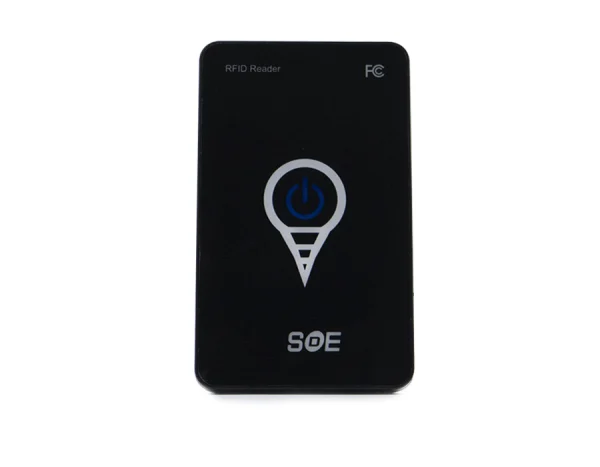
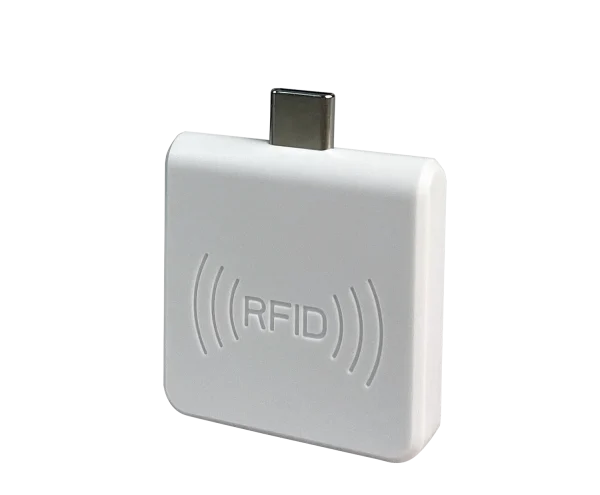
Frequency of operation: 125 kHz
Reading method: automatically
Confirmation of scanning: light and sound signal
Interface: USB
Operating Frequency: 13,56 MHz
Color: blue
Material: ABS
Device Dimensions: 41 x 34 x 5 mm
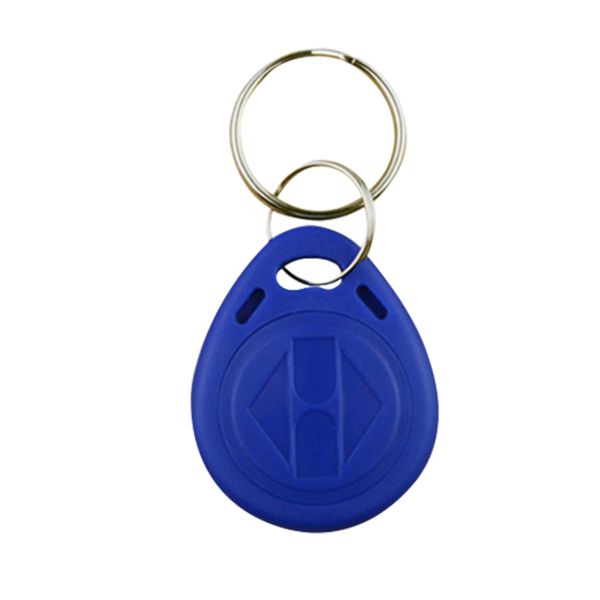
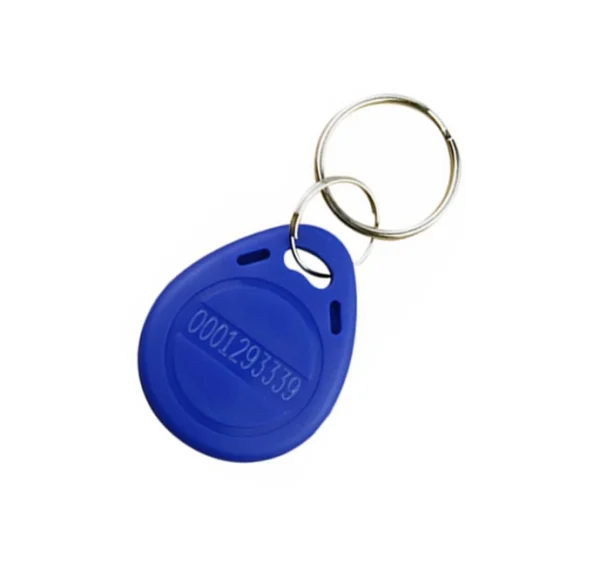
Operating Frequency: 125 kHz
Material: ABS
Color: blue
Device Dimensions: 41 x 34 x 5 mm
Frequency of operation: 125 kHz
Reading method: automatically
Confirmation of reading: light
Power supply: USB DC 5V
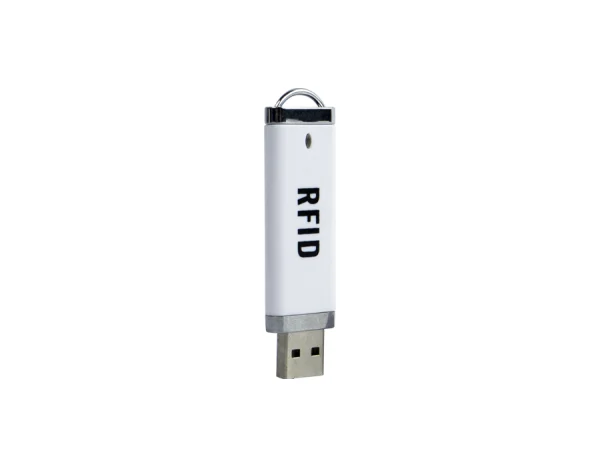
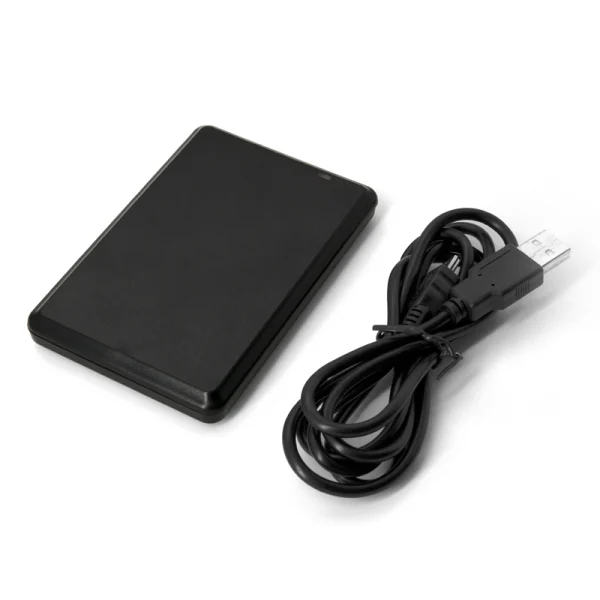
Frequency of operation: 125 kHz
Reading method: automatically
Confirmation of reading: light
Interface: USB
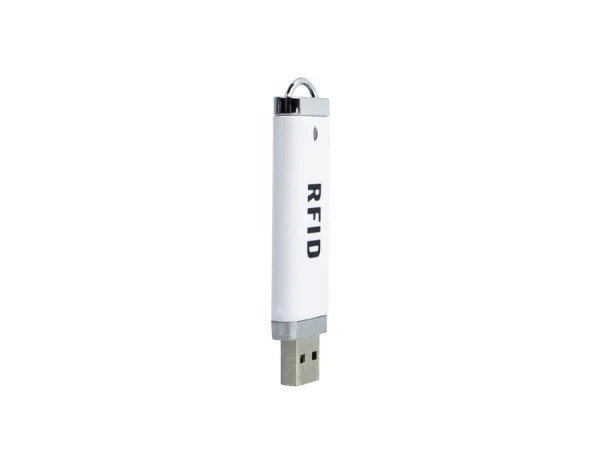
Frequency of operation: 125 kHz
Reading method: automatically
Confirmation of reading: light and sound signal
Readable chip types: EM4100, SMC4001, EM4200, EM4305, T5577
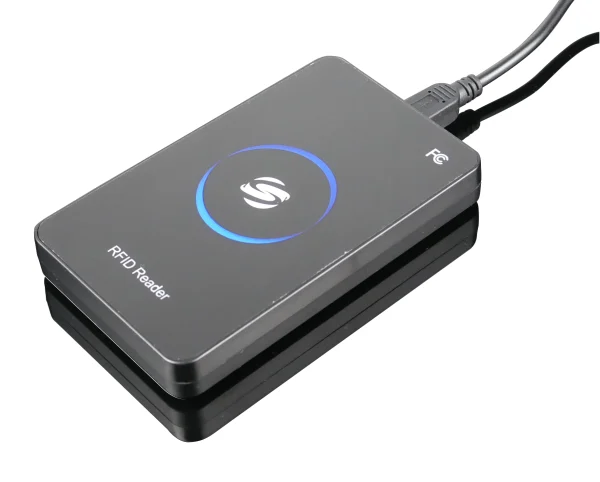
Frequency of operation: 125 kHz
Reading method: automatically
Confirmation of reading: light and sound signal
Power supply: USB DC 5V
Frequency of operation: 125 kHz, 13,56 MHz
Reading method: automatically
Confirmation of reading: light and sound signal
Power supply: USB DC 5V
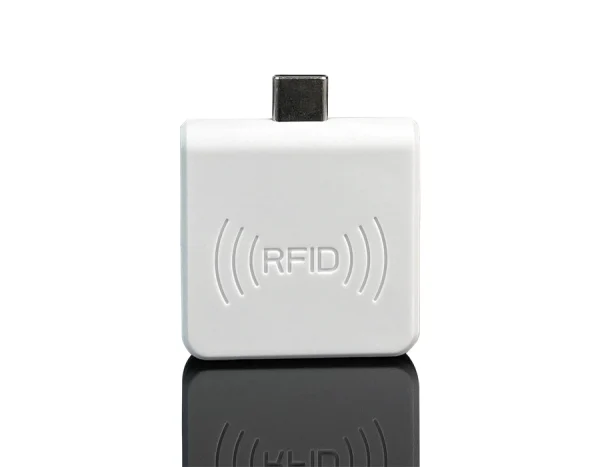
Frequency of operation: 125 kHz
Reading method: automatically
Confirmation of reading: light and sound signal
Reading speed: up to 200 ms
Frequency of operation: 13,56 MHz
Reading speed: up to 200 ms
Reading method: automatically
Power supply: USB DC 5V